| |
|
|
|
|
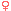 1160 - 1220 (59 years) 1160 - 1220 (59 years)
Generation: 1
| 1. | Alys of France, Countess of Vexin was born 04 Oct 1160 (daughter of King Louis VII of France and Constance of Castile); died ca 1220; was buried , Abbey of Valloires, Picardie, France. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alys_of_France,_Countess_of_Vexin
She was the daughter of King Louis VII of France and his second wife, Constance of Castile. Alys was the half-sister of Marie and Alix of France, Louis's children by Eleanor of Aquitaine, and the younger sister of Margaret of France.
In January 1169, Louis and Henry II of England signed a contract for the marriage between Alys and Henry's son Richard the Lionheart. The 8-year-old Alys was then sent to England as Henry's ward. There were widespread rumors that Henry had not only made Alys his mistress, but that she had borne him a child. Henry died in 1189. King Richard married Berengaria of Navarre on 12 May 1191, while still officially engaged to Alys.
Her brother, King Philip of France, had offered Alys to Prince John, but Eleanor prevented the match. Alys married William IV Talvas, Count of Ponthieu, on 20 August 1195, and had one child Marie, Countess of Ponthieu. She was some eighteen years older than William, and Philip figured that the couple would be childless, and he would thus gain control of Ponthieu, a small but strategically important county. However, when Alys then gave birth to Marie, this child became the heiress to Ponthieu when her father died.
Alys married William (Guillaume) IV (Talvas) of Ponthieu, Count of Ponthieu. William (son of John (Jean) I of Ponthieu, Count of Ponthieu and Beatrice of Saint-Pol) was born ca 1179, Abbeville, Picardie, France; died 04 Oct 1221; was buried , Abbey of Valloires, Picardie, France. [Group Sheet]
Children:
- Marie of Ponthieu, Countess of Ponthieu was born 17 Apr 1199, Abbeville, Picardie, France; died 21 Sep 1250, Abbeville, Picardie, France; was buried , Abbey of Valloires, Picardie, France.
|
Generation: 2
| 2. | King Louis VII of France was born 1120, Paris, France (son of King Louis VI France and Adelaide of Maurienne, de Savoy); died 18 Sep 1180, Saint-Pont, Auvergne, France; was buried , Saint Denis Basilique, Saint-Denis, Île-de-France, France. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Louis_VII_of_France
He was King of the Franks from 1137 until his death. He was the son and successor of King Louis VI of France, hence his nickname, and married Eleanor of Aquitaine, one of the wealthiest and most powerful women in western Europe. Eleanor came with the vast Duchy of Aquitaine as a dowry for Louis, thus temporarily extending the Capetian lands to the Pyrenees, but their marriage was annulled in 1152 after no male heir was produced. They had two daughters, Marie and Alix.
Immediately after the annulment of her marriage, Eleanor married Henry Plantagenet, Duke of Normandy and Count of Anjou, to whom she gave the Aquitaine. When Henry became King of England in 1154, as Henry II, he ruled over a large empire that spanned from Scotland to the Pyrenees. Henry's efforts to preserve and expand on this patrimony for the Crown of England would mark the beginning of the long rivalry between France and England.
Louis VII's reign saw the founding of the University of Paris and the disastrous Second Crusade. Louis and his famous counselor Abbot Suger pushed for a greater centralization of the state and favoured the development French Gothic architecture, notably the construction of Notre-Dame de Paris.
Louis was born in 1120 in Paris, the second son of Louis VI of France and Adelaide of Maurienne. The early education of Prince Louis anticipated an ecclesiastical career. As a result, he became well-learned and exceptionally devout, but his life course changed decisively after the accidental death of his older brother Philip in 1131, when he unexpectedly became the heir to the throne of France. He spent much of his youth in Saint-Denis, where he built a friendship with the Abbot Suger, an advisor to his father who also served Louis well during his early years as king.
In the first part of his reign, Louis VII was vigorous and zealous in his prerogatives. His accession was marked by no disturbances other than uprisings by the burgesses of Orléans and Poitiers, who wished to organise communes. He soon came into violent conflict with Pope Innocent II, however, when the archbishopric of Bourges became vacant.
Louis VII then became involved in a war with Theobald II of Champagne by permitting Raoul I of Vermandois, the seneschal of France, to repudiate his wife, Theobald II's niece, and to marry Petronilla of Aquitaine, sister of the queen of France. He was personally involved in the assault and burning of the town of Vitry-le-François. More than a thousand people who had sought refuge in the church died in the flames. Overcome with guilt and humiliated by ecclesiastical reproach, Louis admitted defeat, removed his armies from Champagne and returned them to Theobald.
Desiring to atone for his sins, he declared his intention of mounting a crusade on Christmas Day 1145. In June 1147, in fulfilment of his vow to mount the Second Crusade, Louis VII and his queen, Eleanor of Aquitaine, set out from the Basilica of St Denis, first stopping in Metz on the overland route to Syria. Just beyond Laodicea, the French army was ambushed by Turks. The French were bombarded by arrows and heavy stones, and the Turks swarmed down from the mountains. Louis VII and his army finally reached the Holy Land in 1148. His queen Eleanor supported her uncle, Raymond of Antioch, and prevailed upon Louis to help Antioch against Aleppo. But Louis VII's interest lay in Jerusalem, but this ended in disaster and the project was abandoned. Louis VII decided to leave the Holy Land, despite the protests of Eleanor, who still wanted to help her doomed uncle Raymond. Louis VII and the French army returned home in 1149.
The expedition to the Holy Land came at a great cost to the royal treasury and military. It also precipitated a conflict with Eleanor that lead to the annulment of their marriage. Perhaps the marriage to Eleanor might have continued if the royal couple had produced a male heir, but this had not occurred. The marriage was annulled on 21 March 1152. The pretext of kinship was the basis for annulment, but in fact, it owed more to the state of hostility between Louis and Eleanor, the decreasing likelihood that their marriage would produce a male heir to the throne of France, and the distinct possibility that Louis had learned of Eleanor's affair with Henry, Count of Anjou.
In 1154, Louis VII married Constance of Castile, daughter of Alfonso VII of Castile. She also failed to supply him with a son and heir, bearing only two daughters, Marguerite and Alys. Constance died in childbirth on 4 October 1160.
Five weeks after the death of Constance, Louis VII married Adèle of Champagne. In 1165, she bore him a son and heir, Philip II Augustus. Louis had him crowned at Reims in 1179, in the Capetian tradition (Philip would in fact be the last king so crowned). Already stricken with paralysis, Louis himself could not be present at the ceremony. He died on 18 September 1180 at the Abbey at Saint-Pont, Allier, and was buried in the Cistercian Abbey of Barbeaux (later moved to Saint-Denis in 1817).
From the point of view of the preservation and expansion of the French royal domains, the reign of Louis VII was a difficult and unfortunate one. Yet royal authority was more strongly felt in the parts of France distant from these domains: more direct and more frequent connections were made with distant vassals, a result largely due to an alliance between the clergy with the crown. Louis VII thus reaped the reward for services rendered the church during the least successful portions of his reign. His greater accomplishments lie in the development of agriculture, population, commerce, the building of stone fortresses, as well as an intellectual renaissance. Considering the significant disparity of political leverage and financial resources between Louis VII and his Angevin rival Henry II, not to mention Henry's superior military skills, Louis VII should be credited with helping to preserve the Capetian dynasty.
Louis' children by his three marriages:
Eleanor of Aquitaine:
1. Marie (1145-11 March 1198), married Henry I of Champagne[
2. Alix (1151-1197/1198), married Theobald V of Blois
Constance of Castile:
3. Margaret (1158-August/September 1197), married a) Henry the Young King; b) King Béla III of Hungary
4. Alys (4 October 1160-ca. 1220), engaged to Richard I of England; she married William IV, Count of Ponthieu
Adele of Champagne:
5. Philip II Augustus (22 August 1165-1223)
6. Agnes (1171-after 1204), who was betrothed to Alexius II Comnenus (1180-1183). but married first Andronicus I Comnenus (1183-1185), then Theodore Branas (1204)
Buried:
Grave location and tomb photo:
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=21090
Louis married Constance of Castile. Constance (daughter of Alfonso VII Raimúndez of León, King of Galicia, King of León and Castille and Berenguela (Berengaria) of Barcelona, Queen of Castille, León and Galicia) was born 1140, Spain; died 04 Oct 1160, Paris, France; was buried , Saint Denis Basilique, Saint-Denis, Île-de-France, France. [Group Sheet]
|
| 3. | Constance of Castile was born 1140, Spain (daughter of Alfonso VII Raimúndez of León, King of Galicia, King of León and Castille and Berenguela (Berengaria) of Barcelona, Queen of Castille, León and Galicia); died 04 Oct 1160, Paris, France; was buried , Saint Denis Basilique, Saint-Denis, Île-de-France, France. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Constance_of_Castile
She was Queen of France as the second wife of Louis VII, who married her following the annulment of his marriage to Eleanor of Aquitaine.[1] She was a daughter of Alfonso VII of León and Berengaria of Barcelona, but her year of birth is not certainly known.
Constance died giving birth to her second child. Desperate for a son, her husband remarried a mere five weeks after her death.
Constance bore her husband two children:
1. Margaret, 1157-1197, who married first Henry the Young King of England, and then Béla III of Hungary
2. Alys, 1160-1220, who married William IV of Ponthieu
Buried:
Grave location, biography and effigy photo:
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=21065
|
Generation: 3
| 4. | King Louis VI France was born 01 Dec 1081, Paris, France (son of Philip I of the Franks, the Amorous and Bertha of Holland); died 01 Aug 1137, Béthisy-Saint-Pierre, France; was buried , Saint Denis Basilica, Paris, France. Notes:
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Louis_VI_of_France
He was the son of of Philip I and his first wife, Bertha of Holland. Louis married Lucienne de Rochefort, a French crown princess, in 1104, but repudiated her three years later. They had no children.
Louis married Adelaide of Maurienne, daughter of Humbert II of Savoy and Gisela of Burgundy, and niece of Pope Callixtus II. They had eight children. Adelaide was one of the most politically active of all France's medieval queens. Her name appears on 45 royal charters from the reign of Louis VI. During her tenure as queen, royal charters were dated with both her regnal year and that of the king.
Louis was the first member of the House of Capet to make a lasting contribution to the centralizing institutions of royal power. He spent almost all of his twenty-nine-year reign fighting either the "robber barons" who plagued Paris or the Norman kings of England for their continental possession of Normandy. Nonetheless, Louis VI managed to reinforce his power considerably and became one of the first strong kings of France since the division of the Carolingian Empire in 843.
When Louis ascended the throne the Kingdom of France was a collection of feudal principalities. Beyond the Isle de France the French Kings had little authority over the great Dukes and Counts of the realm but slowly Louis began to change this and assert Capetian rights. This process would take two centuries to complete but began in the reign of Louis VI.
The second great challenge facing Louis was to counter the rising power of the Anglo-Normans under their capable new King, Henry I of England. Louis was involved with a coalition of Norman and French seigneurs opposed to Henry. The plan was to drive the English King from Normandy and replace him.
Louis was a warrior king but by his forties his weight had become so great that it was increasingly difficult for him to lead in the field.
As Louis VI approached his end there seemed reasons for optimism. He made great strides in exercising his royal authority over his barons. William X, Duke of Aquitaine, on his deathbed, had appointed Louis VI guardian of his fifteen-year-old daughter and heiress, Eleanor of Aquitaine. Eleanor was suddenly the most eligible heiress in Europe and Louis wasted no time in marrying her to his own heir, the future Louis VII. At a stroke Louis had added one of the most powerful Duchies in France to the Capetian domains.
Henry I of England was dead and Stephen of Blois had seized the English Crown, reneging on the oath he had sworn to support Empress Matilda. So England was in turmoil. That was not to last as Matilda married Geoffrey of Anjoy [ Plantagenet] and fought to regain the throne for her son, Henry II. Henry II married Eleanor of Aquitaine and added to the hostilities between France and England for Louis descendants.
Source:
GenealogieOnline. Coret Genealogie. http://www.genealogieonline.nl/en/
Name: Louis VI France
Gender: m (Male)
Birth Date: 1 dec 1081
Birth Place: Paris, France
Death Date: 1 aug 1137
Death Place: Béthisy-Saint-Pierre, France
Death Age: 55
Father: Philip I France
Mother: Bertha Holland
Spouse: Adelaide Maurienne
Children: Louis VII France
Robert I Dreux
Peter Courtenay
Constance France
Buried:
Grave location, biography, historical portraits, and photo of tomb effigy:
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=21089
Louis married Adelaide of Maurienne, de Savoy. Adelaide (daughter of Umberto II of Savoy, the Fat and Gisela of Burgundy, Marchioness of Montferrat) was born 1092, Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne, France; died 18 Nov 1154, Abbey of Montmartre, France; was buried , Church of St. Pierre, Montmartre, France. [Group Sheet]
|
| 5. | Adelaide of Maurienne, de Savoy was born 1092, Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne, France (daughter of Umberto II of Savoy, the Fat and Gisela of Burgundy, Marchioness of Montferrat); died 18 Nov 1154, Abbey of Montmartre, France; was buried , Church of St. Pierre, Montmartre, France. Notes:
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adelaide_of_Maurienne
She was the daughter of Humbert II of Savoy and Gisela of Burgundy and niece of Pope Callixtus II, and became the second wife of Louis VI of France.
They had seven sons and one daughter:
Philip of France (1116-1131)
Louis VII (1120-18 November 1180), King of France
Henry (1121-1175), Archbishop of Reims
Hugues (b. c. 1122)
Robert (c. 1123-11 October 1188), Count of Dreux
Constance (c. 1124-16 August 1176), married first Eustace IV, Count of Boulogne and then Raymond V of Toulouse.
Philip (1125-1161), Bishop of Paris. not to be confused with his elder brother.
Peter (c. 1125-1183), married Elizabeth, Lady of Courtenay
Adelaide was one of the most politically active of all France's medieval queens. Her name appears on 45 royal charters from the reign of Louis VI. Among many other religious benefactions, she and Louis founded the monastery of St Peter's (Ste Pierre) at Montmartre, in the northern suburbs of Paris.
After Louis VI's death, Adélaide did not immediately retire to a convent, as did most widowed queens of the time. Instead she married Matthieu I of Montmorency, with whom she had one child. She remained active in the French court and in religious activities.
In 1153 she retired to the abbey of Montmartre, which she had founded with Louis VII. She died there on 18 November 1154. She was buried in the cemetery of the Church of St. Pierre at Montmartre, but her tomb was destroyed during the French Revolution.
Buried:
Grave location, biography, and tomb photo:
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=36523021
Children:
- 2. King Louis VII of France was born 1120, Paris, France; died 18 Sep 1180, Saint-Pont, Auvergne, France; was buried , Saint Denis Basilique, Saint-Denis, Île-de-France, France.
- Pierre/Peter of France, de Courtenay was born Sep 1126, Reims, France; died 10 Apr 1183, Acre, Holy Land; was buried , Exeter Cathedral, Devon, England.
|
|
| 6. | Alfonso VII Raimúndez of León, King of Galicia, King of León and Castille was born 01 Mar 1105, Caldas de Reis, Galicia, Spain (son of Raymond of Burgundy and Urraca of León, Queen of León, Castile, and Galicia); died 21 Aug 1157, Muradel Pass, Sierra Morena mountains, Spain ; was buried , Cathedral of Toledo, Toledo, Castilla-La Mancha, Spain. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alfonso_VII_of_Le%C3%B3n
The son of Urraca of León and Raymond of Burgundy of the first of the House of Ivrea to rule in the Iberian peninsula, he became the King of Galicia in 1111 and King of León and Castile in 1126. Alfonso first used the title Emperor of All Spain, alongside his mother Urraca, once his mother vested him with the direct rule of Toledo in 1116.
Alfonso was a dignified and somewhat enigmatic figure. He also sought to make the imperial title meaningful in practice, though his attempts to rule over both Christian and Muslim populations was even less successful. During his tenure, Portugal became de facto independent, in 1128, and was recognized as de jure independent, in 1143. He was a patron of poets, including, probably, the troubadour Marcabru.
In 1111, Alfonso was crowned King of Galicia in the cathedral of Santiago de Compostela. He was a child, but his mother had in 1109 succeeded to the united throne of León-Castile-Galicia and desired to assure her son's prospects and groom him for his eventual succession.
By 1125 he had inherited the formerly Muslim Kingdom of Toledo. On 10 March 1126, after the death of his mother, he was crowned in León and immediately began the recovery of the Kingdom of Castile, which was then under the domination of Alfonso the Battler, King of Navarre and Aragón. By the Peace of Támara of 1127, the Battler recognised Alfonso VII as King of Castile. This territory had gained much independence during the rule of his mother and experienced many rebellions. After his recognition in Castile, Alfonso fought to curb the autonomy of the local barons.
In 1135, Alfonso was crowned "Emperor of Spain" in the Cathedral of León. By this, he probably wished to assert his authority over the entire peninsula and his absolute leadership of the Reconquest. He appears to strive for the formation of a national unity which Spain had never possessed since the fall of the Visigothic kingdom.
Alfonso was a pious prince. He introduced the Cistercians to Iberia by founding a monastery at Fitero. He adopted a militant attitude towards the Moors of Andalusia and led a series of crusades subjugating the Moors. By 1144, he advanced as far as Córdoba.
When Pope Eugene III preached the Second Crusade, Alfonso VII, with García Ramírez of Navarre and Ramon Berenguer IV, led a mixed army of Catalans and Franks, with a Genoese?Pisan navy, in a crusade against the rich Mediterranean port city of Almería, in Andalusia, which was occupied in October 1147. Six years later, Almería entered into Moorish possession again. Alfonso was returning from an expedition against them when he died in pass of Muradel in the Sierra Morena mountains.
Alfonso was at once a patron of the church and a protector, though not a supporter of, the Moors, who were a minority of his subjects. His reign ended in an unsuccessful campaign against the rising power of the Muslim Almohads. Though he was not actually defeated, his death in the pass, while on his way back to Toledo, occurred in circumstances which showed that no man could be what he claimed to be, "king of the men of the two religions." Furthermore, by dividing his realm between his sons, he ensured that Christendom would not present the new Almohad threat with a united front.
In November 1128, he married Berenguela, daughter of Ramon Berenguer III, Count of Barcelona. She died in 1149. Their children were:
1. Sancho III of Castile (1134-1158)
2. Ramon, living 1136, died in infancy
3. Ferdinand II of León (1137-1188)
4. Constance (c.1138-1160), married Louis VII of France
5. Sancha (c.1139-1179), married Sancho VI of Navarre
6. García (c.1142-1145/6)
7. Alfonso (c.1144-by 1149)
In 1152, Alfonso married Richeza of Poland, the daughter of Ladislaus II the Exile. They had:
8. Ferdinand, (1153-1157)
9. Sancha (1155-1208), the wife of Alfonso II of Aragón.
Alfonso also had two mistresses, having children by both. By an Asturian noblewoman named Guntroda Pérez, he had an illegitimate daughter, Urraca (1132-1164), who married García Ramírez of Navarre, the mother retiring to a convent in 1133.
Later in his reign, he formed a liaison with Urraca Fernández, widow of count Rodrigo Martínez and daughter of Fernando Garcés de Hita, an apparent grandson of García Sánchez III of Navarre, having a daughter Stephanie the Unfortunate (1148-1180), who was killed by her jealous husband, Fernán Ruiz de Castro.
Buried:
Grave location, biography, and historical portraits:
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=88303926
Alfonso married Berenguela (Berengaria) of Barcelona, Queen of Castille, León and Galicia. Berenguela (daughter of Ramon Berenguer, III of Barcelona, Count of Barcelona, Girona, and Ausona , and Count of Provence and Douce I of Provence, Countess of Provence) was born ca 1116, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain; died 15 Jan 1149, Palencia, Castile and León, Spain; was buried , Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela Santiago de Compostela Provincia da La Coruña Galicia, Spain. [Group Sheet]
|
| 7. | Berenguela (Berengaria) of Barcelona, Queen of Castille, León and Galicia was born ca 1116, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain (daughter of Ramon Berenguer, III of Barcelona, Count of Barcelona, Girona, and Ausona , and Count of Provence and Douce I of Provence, Countess of Provence); died 15 Jan 1149, Palencia, Castile and León, Spain; was buried , Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela Santiago de Compostela Provincia da La Coruña Galicia, Spain. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berengaria_of_Barcelona
Berenguela or Berengaria of Barcelona was Queen consort of Castile, León and Galicia. She was the daughter of Raimon III of Barcelona and Dulce Aldonza Milhaud. Berenguela was the sister of Ramon Berenguer IV who was the ruler of the Kingdom of Aragon.
In November 1128, she married Alfonso VII. Their children were:
1. Sancho III of Castile (1134-1158)
2. Ramon, living 1136, died in infancy
3. Ferdinand II of León (1137-1188)
4. Constance (c.1138-1160), married Louis VII of France
5. Sancha (c.1139-1179), married Sancho VI of Navarre
6. García (c.1142-1145/6)
7. Alfonso (c.1144-by 1149)
In her lifetime a new political entity was formed in the northeast Iberian Peninsula: Portugal seceded from León in the west, giving more balance to the Christian kingdoms of the Iberian peninsula. Her brother Ramon Berenguer successfully pulled Aragon out of its pledged submission to Castile, aided no doubt by the beauty and charm of his sister Berengaria, for which she was well known in her time.
Her niece Dulce of Aragon married Sancho I of Portugal, while her famous granddaughter was Queen Berengaria of England.
She died in Palencia, and was buried at the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela.
Buried:
Grave location, biography, photos of effigy and cathedral:
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=90699229
Children:
- Ferdinand II of León was born ca 1137, Toledo, Castilla-La Mancha, Spain; died 22 Jan 1188, Benavente, Zamora, Spain; was buried , Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela Santiago de Compostela Provincia da La Coruña Galicia, Spain.
- 3. Constance of Castile was born 1140, Spain; died 04 Oct 1160, Paris, France; was buried , Saint Denis Basilique, Saint-Denis, Île-de-France, France.
|
|
Generation: 4
| 8. | Philip I of the Franks, the Amorous was born 23 May 1052, Champagne-et-Fontaine, France (son of Henry I of France and Anna Agnesa Yaroslavna of Kiev); died 29 Jul 1108, Melun, Seine-et-Marne, Île-de-France, France; was buried , Saint-Benoît-sur-Loire, France. Notes:
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philip_I_of_France
Unusual at the time for Western Europe, his name was of Greek origin, being bestowed upon him by his mother. Although he was crowned king at the age of seven, until age fourteen (1066) his mother acted as regent, the first queen of France ever to do so.
The was called the Amorous because of his marital difficulties.
Philip first married Bertha of Holland in 1072. Although the marriage produced the necessary heir, Philip fell in love with Bertrade de Montfort, the wife of Fulk IV, Count of Anjou. He repudiated Bertha (claiming she was too fat) and married Bertrade on 15 May 1092. He was excommunicated by Pope Urban II. Several times the ban was lifted as Philip promised to part with Bertrade, but he always returned to her, but in 1104 Philip made a public penance and must have kept his involvement with Bertrade discreet.
A great part of his reign, like his father's, was spent putting down revolts by his power-hungry vassals. In 1077, he made peace with William the Conqueror, who gave up attempting the conquest of Brittany.
Buried:
Grave location, biography, portrait and effigy:
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=53676134&ref=acom
Philip married Bertha of Holland. Bertha (daughter of Floris I of Holland and Gertrude of Saxony) was born ABT. 1055, Vlaardingen, Netherlands; died 30 Jul 1093, Montreuil, Pas-de-Calais, Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France. [Group Sheet]
|
| 9. | Bertha of Holland was born ABT. 1055, Vlaardingen, Netherlands (daughter of Floris I of Holland and Gertrude of Saxony); died 30 Jul 1093, Montreuil, Pas-de-Calais, Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France. Notes:
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bertha_of_Holland
Also known as Berthe or Bertha of Frisia,Bertha was the daughter of Count Floris I of Holland and his wife, Gertrude of Saxony. Her father ruled a territory vaguely described as "Friesland west of the Vlie", which is where Bertha spent her childhood. He was assassinated in 1061, and and two years later her mother remarried Count Robert the Frisian of Flanders.
Her stepfather became involved in a war with King Philip I of France over succession to the County of Flanders. Bertha was given in marriage to King Philip as part of the peace negotiations. At the time, she was the lowest ranking woman to marry a French king.
Bertha was queen consort of the Franks from 1072 until 1092. She did not have a happy marriage. After six years of childlessness, the royal couple had three children, including Philip's successor, Louis VI, the Fat, Constance, Princess of Antioch [married Bohemund I of Antioch] and Henry, but he appears to have died in infancy or childhood.
Philip, however, grew tired of his wife by 1090, and repudiated her in 1092 in order to marry the already married Bertrada of Montfort. That marriage was a scandal since both Philip and Bertrada were already married to other people.
The marriage began breaking apart. The King became tired of his wife but the reasons are unclear. Contemporary chroniclers give different explanations. According to the English historian William of Malmesbury, Philip complained that Bertha was "too fat", though he was himself becoming too obese to ride a horse.
The repudiated queen withdrew to the fortress of Montreuil-sur-Mer, which was part of her dower land where she died in 1093. The son of the queen who had been repudiated ostensibly for her obesity ascended the French throne as Louis VI. He was known as Louis, the Fat. Berta's nephew and King Louis' cousin, Count Floris II of Holland, was also nicknamed "the Fat."
Children:
- 4. King Louis VI France was born 01 Dec 1081, Paris, France; died 01 Aug 1137, Béthisy-Saint-Pierre, France; was buried , Saint Denis Basilica, Paris, France.
|
|
| 10. | Umberto II of Savoy, the Fat was born 1065, County of Savoy (son of Amadeus II of Savoy and Joan of Geneva); died 19 Oct 1103, County of Savoy. Notes:
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Humbert_II,_Count_of_Savoy
Nicknamed the Fat, he was he son of Amadeus II of Savoy.
The County and later Duchy of Savoy was a territory is shared between the modern countries of France, Italy, and Switzerland. The House of Savoy became the longest surviving royal house in Europe. It ruled the County of Savoy from 1003 to 1416 and then the Duchy of Savoy from 1416 to 1860.
He was married to Gisela of Burgundy, daughter of William I, Count of Burgundy, and had 7 children:
Amadeus III of Savoy
William, Bishop of Liège
Adelaide, (d. 1154), married to Louis VI of France
Agnes, (d. 1127), married to Archimbald VI, lord of Bourbon
Umberto
Reginald
Guy, abbey of Namur
Umberto married Gisela of Burgundy, Marchioness of Montferrat. Gisela (daughter of William I Count of Burgundy, the Great and Stephanie) was born 1075, County of Burgundy; died May 1135, Montferrat, Italy. [Group Sheet]
|
| 11. | Gisela of Burgundy, Marchioness of Montferrat was born 1075, County of Burgundy (daughter of William I Count of Burgundy, the Great and Stephanie); died May 1135, Montferrat, Italy. Notes:
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gisela_of_Burgundy,_Marchioness_of_Montferrat
Daughter of William I, Count of Burgundy, she was the wife of Humbert II, Count of Savoy and later of Rainier I of Montferrat.
With Humbert II of Savoy her children included:
Amadeus III of Savoy
William, Bishop of Liège
Adelaide of Maurienne (d. 1154), wife of King Louis VI of France
Agnes, (d. 1127), wife of Arcimboldo VI, lord of Bourbon
Humbert
Reginald
Guy, Abbot of Namur
------------
GenealogieOnline. Coret Genealogie. http://www.genealogieonline.nl/en
Name: Gisela Burgundy
Gender: f (Female)
Birth Date: 1075
Death Date: 1133
Death Age: 58
Father: William I Burgundy
Mother: Stephanie Nn
Spouse: Humbert II Savoy
Renier I Montferrat
Children: Adelaide Maurienne
Agnes Maurienne
William V Montferrat
Amadeus Savoy
Children:
- 5. Adelaide of Maurienne, de Savoy was born 1092, Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne, France; died 18 Nov 1154, Abbey of Montmartre, France; was buried , Church of St. Pierre, Montmartre, France.
- Amadeus III of Savoy was born ca 1095, Carignano, Piedmont, Italy; died Apr 1148, Nicosia, Cyprus; was buried , Saint Croix, Strovolos Nicosia, Cyprus.
|
|
| 12. | Raymond of Burgundy was born ca 1070, Besançon, County of Burgundy, France; died 24 May 1107, Grajal de Campos, Provincia de León Castilla y León, Spain; was buried , Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela Santiago de Compostela Provincia da La Coruña Galicia, Spain. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raymond_of_Burgundy
The fourth son of Count William I of Burgundy and Stephanie, he was was the ruler of Galicia from about 1090 until his death.
When Raymond and his cousin, Henry of Burgundy, first arrived in Spain is uncertain, but it probably it was with the army of Duke Odo I of Burgundy in 1086, to prosecute the Reconquest against the Muslims. Most of the army returned home, but Odo and his retinue went west. By 21 July 1087 they were probably at Burgos, at the court of Alfonso VI, and by 5 August he was in the capital city of León. There Odo arranged Raymond's marriage to Alfonso's heiress, Urraca.
By his marriage Raymond received as dowry the government of the Kingdom of Galicia (which included the County of Portugal and the County of Coimbra), although shortly after, in 1095, Alfonso VI gave the County of Portugal and the County of Coimbra to Henry of Burgundy, father of the first Portuguese King Afonso Henriques of Portugal. During his government Raymond was titled Count, Dominus, Prince, Emperor and Consul of Galicia or of the Galicians, exercising near absolute power in his domains.
He died at the castle of Grajal de Campos after a short illness. He was father of Alfonso VII of León and Castile.
Buried:
Grave location, historical portrait, and photo of cathedral:
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=67221138
Raymond married Urraca of León, Queen of León, Castile, and Galicia. Urraca (daughter of Alfonso VI of León and Castile, King of León, Castille and Galicia and Constance of Burgundy, Queen of Castile and Léon) was born Apr 1079, Burgos, Provincia de Burgos, Castilla y León, Spain; died 08 Mar 1126, Saldaña, Provincia de Burgos, Castilla y León, Spain; was buried , Basilica Of San Isidoro, León, Provincia de León, Castilla y León, Spain. [Group Sheet]
|
| 13. | Urraca of León, Queen of León, Castile, and Galicia was born Apr 1079, Burgos, Provincia de Burgos, Castilla y León, Spain (daughter of Alfonso VI of León and Castile, King of León, Castille and Galicia and Constance of Burgundy, Queen of Castile and Léon); died 08 Mar 1126, Saldaña, Provincia de Burgos, Castilla y León, Spain; was buried , Basilica Of San Isidoro, León, Provincia de León, Castilla y León, Spain. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urraca_of_Le%C3%B3n
Born in Burgos, Urraca was the eldest and only surviving child of Alfonso VI of León with his second wife Constance of Burgundy; for this, she was heiress presumptive of the Kingdoms of Castile and León until 1107, when her father recognized his illegitimate son Sancho as his heir.
Urraca?s place in the line of succession made her the focus of dynastic politics, and she became a child bride at age eight (1087) to Raymond of Burgundy, a mercenary adventurer. Author Bernard F. Reilly suggests that, rather than a betrothal, the eight-year-old Urraca was fully wedded to Raymond of Burgundy, as he almost immediately appears in protocol documents as Alfonso VI's son-in-law, a distinction that would not have been made without the marriage. Reilly doubts that the marriage was consummated until Urraca was 13, as she was placed under the protective guardianship of a trusted magnate. Her pregnancy and stillbirth at age 14 suggest that the marriage was indeed consummated when she was 13 or 14 years old.
Urraca's marriage to Raymond was part of Alfonso VI's diplomatic strategy to attract cross-Pyrenees alliances, and she gave birth two children: a daughter, Sancha Raimúndez and a son, Alfonso Raimúndez, who would become Alfonso VII. However, Raymond died in 1107, leaving Urraca a widow with two small children.
Urraca became again an heiress presumptive after the death of her brother Sancho at the Battle of Uclés in 1108. Alfonso VI reunited the nobles of the Kingdom in Toledo and announced that his widowed daughter was the chosen one to succeeded him.
The nobles agreed with the royal designation but demanded that Urraca should marry again. Several candidates for the hand of the heiress to the thrones of León and Castile appeared immediately. Alfonso VI feared that the rivalries between Castilian and Leonese nobles would be increased if she married any of these suitors and decided that his daughter should wed Alfonso I of Aragon, known as the Battler, opening the opportunity for uniting León-Castile with Aragon.
Marriage negotiations were still underway when Alfonso VI died on 29 June/1 July 1109 and Urraca became queen. Many of Alfonso VI?s advisers and leading magnates in the kingdom formed a ?quiet opposition? to the marriage of the queen to the King of Aragon. According to Bernard F. Reilly, these magnates feared the influence the King of Aragon might attempt to wield over Urraca and over Leonese politics.
Urraca protested against the marriage but honored her late father's wishes (and the Royal Council's advice) and continued with the marriage negotiations, though she and her father's closest advisers were growing weary of Alfonso I's demands. Despite the advisers' opposition, the prospect of Count Henry of Portugal filling any power vacuum led them to go ahead with the marriage which took place in early October 1109 at the Castle of Monzón de Campos. As events unfolded, these advisers underestimated Urraca's political prowess, and later advised her to end the marriage.
The marriage of Urraca and Alfonso I almost immediately sparked rebellions in Galicia and scheming by her illegitimate half-sister Theresa and brother-in-law Henry, the Countess and Count of Portugal. Also, they believed that the new marriage of Urraca could put in jeopardy the rights of the son of her first marriage, Alfonso Raimúndez.
The Galician rebellion against the royal power was only the beginning of a series of political and military conflicts which, with the complete opposite personalities of Urraca and Alfonso I and their mutual dislike, gave rise to a continuous civil war in the Hispanic kingdoms over the following years.
As their relationship soured, Urraca accused Alfonso of physical abuse, and by May 1110 she separated from Alfonso. Additionally, as Urraca was married to someone many in the kingdom objected to, the queen's son and heir became a rallying point for opponents to the marriage.
Estrangement between husband and wife escalated from discrete and simmering hostilities into open armed warfare between the Leonese-Castilians and the Aragonese. By the fall of 1112 a truce was brokered between Urraca and Alfonso with their marriage annulled. Though Urraca recovered Asturias, Leon, and Galicia, Alfonso occupied a significant portion of Castile (where Urraca enjoyed large support), while her half-sister Theresa and her husband Count Henry of Portugal occupied Zamora and Extremadura. Recovering these regions and expanding into Muslim lands would occupy much of Urraca's foreign policy.
She is characterized in her contemporary history Historia Compostelana as prudent, modest, and with good sense. But this source also attributes her "failings" to her gender, "the weakness and changeability of women, feminine perversity, and calls her a Jezebel" for her liaisons with her leading magnates, with at least one relationship producing an illegitimate son. The measure of success for Urraca?s rule was her ability to restore and protect the integrity of her inheritance, that is, the kingdom of her father, and transmit that inheritance in full to her own heir.
Children:
- 6. Alfonso VII Raimúndez of León, King of Galicia, King of León and Castille was born 01 Mar 1105, Caldas de Reis, Galicia, Spain; died 21 Aug 1157, Muradel Pass, Sierra Morena mountains, Spain ; was buried , Cathedral of Toledo, Toledo, Castilla-La Mancha, Spain.
|
|
| 14. | Ramon Berenguer, III of Barcelona, Count of Barcelona, Girona, and Ausona , and Count of Provence was born 11 Nov 1082, Rodez, Toulouse, France; died 19 Aug 1131, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain; was buried , Santa Maria de Ripoll, Ripoll, Provincia de Girona, Catalonia, Spain. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ramon_Berenguer_III,_Count_of_Barcelona
Ramon Berenguer III the Great was the count of Barcelona, Girona, and Ausona, Besalú, Cerdanya, and count of Provence in the Holy Roman Empire until his death in Barcelona in 1131. As Ramon Berenguer I, he was Count of Provence from 1112 in right of his wife.
Born on 11 November 1082 in Rodez, Viscounty of Rodez, County of Toulouse, Francia, he was the son of Ramon Berenguer II.
During his rule Catalan interests were extended on both sides of the Pyrenees. By marriage or vassalage he incorporated into his realm almost all of the Catalan counties (except Urgell and Peralada). He inherited the counties of Besalú and Cerdanya and in between married Douce, heiress of Provence. His dominions then stretched as far east as Nice.
He also established relations with the Italian maritime republics of Pisa and Genoa, and in 1114 and 1115 attacked with Pisa the then-Muslim islands of Majorca and Ibiza.[1] They became his tributaries and many Christian slaves there were recovered and set free. Ramon Berenguer also raided mainland Muslim dependencies with Pisa's help, such as Valencia, Lleida and Tortosa. By 1118 he had captured and rebuilt Tarragona, which became the metropolitan seat of the church in Catalonia.
Toward the end of his life he became a Templar. He gave his five Catalonian counties to his eldest son Ramon Berenguer IV and Provence to the younger son Berenguer Ramon.
He died on 23 January/19 July 1131 and was buried in the Santa Maria de Ripoll monastery.
Ramon's first wife was María Rodríguez de Vivar, second daughter of El Cid (died ca. 1105). They had one child, María, who married Bernat III, Count of Besalú. His second wife Almonds produced no children.
His third wife was Douce, heiress of Provence (died ca. 1127) had at least six children who lived to adulthood:
1. Ramon Berenguer IV, Count of Barcelona (1113/1114-1162) married Petronilla of Aragon, daughter of Ramiro II, King of Aragon.
2. Berenguer Ramon I, Count of Provence (ca. 1115?1144)
3. Berenguela or Berengaria (1116-1149), married Alfonso VII of Castile
4. Jimena (1117-1136), also known as Eixemena, married Roger III, Count of Foix
5. Estefania (b. 1118), married Centule II, Count of Bigorre
6. Almodis, married Ponce de Cervera
Ramon married Douce I of Provence, Countess of Provence. Douce was born ca 1090, Provence, France; died 1127. [Group Sheet]
|
| 15. | Douce I of Provence, Countess of Provence was born ca 1090, Provence, France; died 1127. Notes:
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Douce_I,_Countess_of_Provence
She was the daughter of Gilbert I of Gévaudan and Gerberga of Provence and wife of Ramon Berenguer III, Count of Barcelona. In 1112, she inherited the county of Provence through her mother. She married Ramon Berenguer at Arles on 3 February that year.
In 1113, Douce ceded her rights in Provence, Gévaudan, and the viscounty of Millau to her husband. According to a once prevailing opinion, "Provençal troubadours ... entered Catalonia at the time" and even the Catalan language was imported from Provence. It was the beginning of a great scheme to unite various lands on both sides of the Pyrenees.
In reality the marriage gave the House of Barcelona extensive interests in southern France and put it in conflict with the Counts of Toulouse, with whom a partition of Provence was signed in 1125, shortly before Douce's death. Her death inaugurated a period of instability in Provence. A branch of the House of Barcelona was set up to rule, but a disputed succession opened up wars between 1144 through 1162, which terminated in Provençal victory.
Her children with Ramon Berenguer were:
1. Almodis, married Ponce de Cervera
2. Berenguela (1116-1149), married Alfonso VII of Castile
3. Ramon Berenguer (1113-1162), Count of Barcelona
4. Berenguer Ramon (c. 1115-1144), Count of Provence
Children:
- 7. Berenguela (Berengaria) of Barcelona, Queen of Castille, León and Galicia was born ca 1116, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain; died 15 Jan 1149, Palencia, Castile and León, Spain; was buried , Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela Santiago de Compostela Provincia da La Coruña Galicia, Spain.
|
|
|
|
|

